来自:https://www.atlantic.net/vps-hosting/how-to-install-and-configure-parse-server-on-ubuntu-20-04/
#sudo -i
# sudo apt-get update
# sudo apt update
Step 1 – Install MongoDB
- sudo service mongodb start 这是启动命令,以后会用到,现在不需要
- sudo service mongodb stop
- sudo service mongodb restart
- ubuntu环境下使用apt-get命令安装MongoDB
- 查看配置文件信息,默认mongodb 配置文件存放在
- sudo vim /etc/mongodb.conf。
By default, MongoDB is available in the Ubuntu 20.04 default repository. You can install it by running the following command:
apt-get install mongodb-server -y
Once the MongoDB is installed, you can verify the status of MongoDB with the following command:
systemctl status mongodb
You should see the following output:
● mongodb.service – An object/document-oriented database Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mongodb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-08-06 07:32:44 UTC; 30s ago Docs: man:mongod(1) Main PID: 3222 (mongod) Tasks: 23 (limit: 4691) Memory: 42.0M CGroup: /system.slice/mongodb.service └─3222 /usr/bin/mongod –unixSocketPrefix=/run/mongodb –config /etc/mongodb.conf Aug 06 07:32:44 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started An object/document-oriented database.
Step 2 – Install Node.js
First, install the necessary dependencies using the following command.
apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg
Next, download the Node.js GPG key.
mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | gpg –dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg
Next, add the NodeSource repo to the APT source list.
echo “deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_18.x nodistro main” | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list
Then, update the repository index and install the Ndoe.js with the following command.
apt update apt-get install -y nodejs
Next, verify the Node.js version using the following command.
node -v
Output.
v18.19.0
Step 3 – Install Parse Server
# npm install –global yarn
You can install the parse-server module using the Yarn package manager as shown below:
yarn global add parse-server
Once installed, you will need to create a parse server configuration file and define the attributes of the parse server. You can create it with the following command:
nano config.json
Add the following lines:
{ “appName”: “My Parse Server”, “databaseURI”: “mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/parsedb”, “appId”: “K”, “masterKey”: “L”, “serverURL”: “https://ip:1337/parse”, “publicServerURL”: “https://ip:1337/parse”, “port”: 1337,
“masterKeyIps”:[“0.0.0.0”],
“maintenanceKeyIps”:[“0.0.0.0”] }
Save and close the file then start the parse server using the following command:
nohup parse-server config.json &
At this point, the parse server is started and listening on port 1337. You can verify it with the following command:
ss -ant | grep 1337
You should get the following output:
LISTEN 0 511 0.0.0.0:1337 0.0.0.0:* TIME-WAIT 0 0 127.0.0.1:1337 127.0.0.1:40568
Step 4 – Configure Parse Server Dashboard
Parse server comes with a powerful dashboard that allows you to access the Parse server through a web browser. You can install the parse dashboard with the following command:
yarn global add parse-dashboard
After installing the Parse dashboard, create a configuration file for the Parse dashboard with the following command:
nano parse-darshboard-config.json
Add the following lines:
{ “apps”: [ { “serverURL”: “http://your-server-ip:1337/parse”, “appId”: “K”, “masterKey”: “L”, “allowInsecureHTTP”: “true”, “appName”: “MyApp1”,
“masterKeyIps”:[“0.0.0.0”],
“maintenanceKeyIps”:[“0.0.0.0”] } ], “users”: [ { “user”:”admin”, “pass”:”yourpassword” } ], “iconsFolder”: “icons” }
Save and close the file, then start the Parse dashboard with the following command:
nohup parse-dashboard –dev –config parse-darshboard-config.json &
At this point, the Parse dashboard is started and listening on port 4040. You can verify it with the following command:
ss -ant | grep 4040
You should get the following output:
LISTEN 0 511 0.0.0.0:4040 0.0.0.0:*
Step 5 – Verify Parse Server——这一步可以忽略
At this point, the Parse server is installed and configured. Now, perform some tests to make sure it’s running.
First, add some values to the Parse server with the following command:
curl -X POST -H “X-Parse-Application-Id: KSDJFKASJFI3S8DSJFDH” -H “Content-Type: application/json” -d ‘{“score”:1337,”InventoryName”:”Desktops”,”cheatMode”:false}’ http://localhost:1337/parse/classes/Inventory
You should get the following output:
{“objectId”:”BCq9j8fPfM”,”createdAt”:”2020-08-06T07:48:14.530Z”}
Now, fetch the value from the Parse server using the following command:
curl -X GET -H “X-Parse-Application-Id: KSDJFKASJFI3S8DSJFDH” http://localhost:1337/parse/classes/Inventory/BCq9j8fPfM
You should get the following output:
{“objectId”:”BCq9j8fPfM”,”score”:1337,”InventoryName”:”Desktops”,”cheatMode”:false,”createdAt”:”2020-08-06T07:48:14.530Z”,”updatedAt”:”2020-08-06T07:48:14.530Z”}
Step 6 – Access Parse Server Dashboard
You can also access the parse server dashboard by visiting the URL
http://your-server-ip:4040 in your web browser.
You should see the following screen:
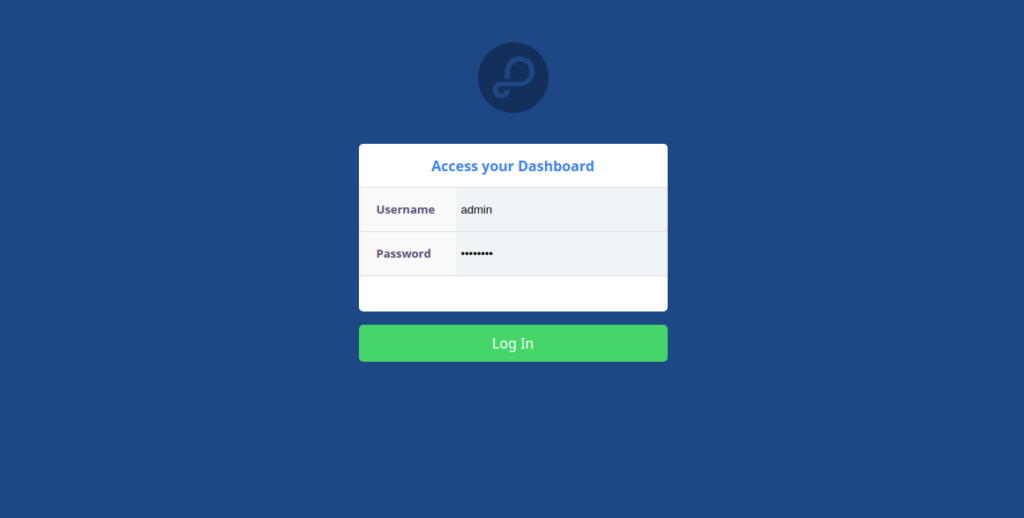
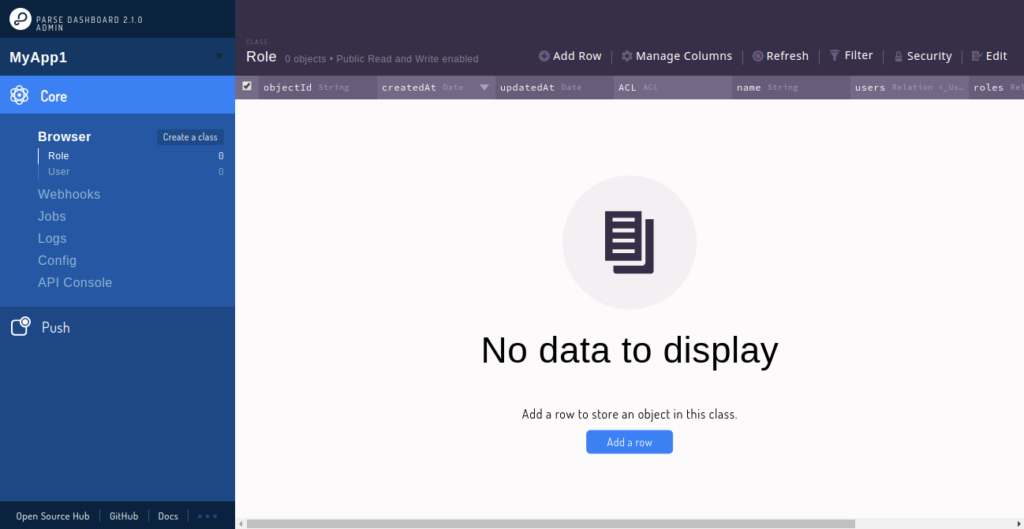
Provide your admin username and password which you have defined in the Parse dashboard configuration file and click on the Log in button. You should see the Parse server dashboard in the following screen:
系统重启后
sudo service mongodb start
cd root
nohup parse-server config.json &
nohup parse-dashboard --dev --config parse-darshboard-config.json &
